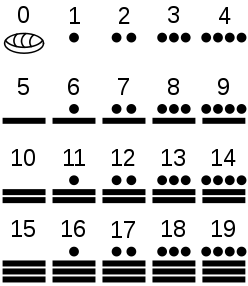
In common with the other Mesoamerican civilizations, the Maya used a base 20 (vigesimal) and base 5 numbering system. Also, the preclassic Maya and their neighbors independently developed the concept of zero by 36 BC. Inscriptions show them on occasion working with sums up to the hundreds of millions and dates so large it would take several lines just to represent it. They produced extremely accurate astronomical observations; their charts of the movements of the moon and planets are equal or superior to those of any other civilization working from naked eye observation.
The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Preclassic period (c. 2000 BC to 250 AD), many Maya cities reached their highest state development during the Classic period (c. 250 AD to 900 AD), and continued throughout the Postclassic period until the arrival of the Spanish. At its peak, it was one of the most densely populated and culturally dynamic societies in the world. [1]
The Maya civilization shares many features with other Mesoamerican civilizations due to the high degree of interaction and cultural diffusion that characterized the region. Advances such as writing, epigraphy, and the calendar did not originate with the Maya; however, their civilization fully developed them. Maya influence can be detected from Honduras, Guatemala, El Salvador and to as far as central Mexico, more than 1000 km (625 miles) from the Maya area. Many outside influences are found in Maya art and architecture, which are thought to result from trade and cultural exchange rather than direct external conquest. The Maya peoples never disappeared, neither at the time of the Classic period decline nor with the arrival of the Spanish conquistadores and the subsequent Spanish colonization of the Americas. Today, the Maya and their descendants form sizable populations throughout the Maya area and maintain a distinctive set of traditions and beliefs that are the result of the merger of pre-Columbian and post-Conquest ideologies (and structured by the almost total adoption of Roman Catholicism). Many Mayan languages continue to be spoken as primary languages today; the Rabinal Achí, a play written in the Achi’ language, was declared a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO in 2005.






